The High Stakes of Compliance in Health Apps
The global digital health market is projected to reach $586 billion by 2030, driven by the rising demand for remote healthcare, telemedicine, and personalized wellness solutions. However, this rapid growth comes with increased regulatory scrutiny. Health and wellness apps collect highly sensitive user data, making them prime targets for data breaches, regulatory fines, and legal action. The best way to address this as a business is to educate yourself on compliance for health app developers.
The global digital health market is projected to reach $586 billion by 2030
Vantage Market Research
For developers and startups that deal with health data, HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) compliance isn’t just a legal requirement—it’s a business advantage that builds trust, ensures longevity, and opens up new market opportunities.
We’ll explore why compliance should be seen as an asset, not just a burden, and how startups that invest in strong security and privacy measures are better positioned for success.
Compliance as a Growth Driver for Health Apps
How Non-Compliance Hurts Business Growth
Many startups approach compliance reactively—only addressing HIPAA and GDPR when problems arise. However, non-compliance has serious consequences:
- Regulatory Fines & Legal Action
- Google was fined €50M ($57M) under GDPR in 2019 for lack of transparency in how it collected health-related data.
- Anthem Inc. paid a $16M HIPAA fine in 2018 after a breach exposed 79 million patient records.
- Loss of Investor Confidence
- Startups with weak data security measures struggle to secure funding.
- Venture capitalists now prioritize privacy-first business models to mitigate risk.
- User Trust & Retention Issues
- 75% of users say they won’t use a health app if they don’t trust how it handles their data.
- Example: The MyFitnessPal breach in 2018 led to 150M user accounts being compromised, causing a significant drop in user engagement.
Health startups that proactively implement compliance measures are seen as more reliable by investors, users, and regulatory bodies, leading to better funding opportunities and long-term growth.
The Business Case for HIPAA & GDPR Compliance
Expanding into New Markets (EU & US Regulations)
Compliance enables global market expansion, especially into the U.S. and European healthcare sectors:
- HIPAA Compliance = U.S. Healthcare Market Access
- U.S. hospitals, insurance providers, and telemedicine companies only partner with HIPAA-compliant apps.
- Example: Teladoc Health, a major telemedicine provider, follows HIPAA to ensure smooth integration with U.S. healthcare systems.
- GDPR Compliance = European Market Expansion
- Any app handling data from EU citizens must comply with GDPR, even if based outside Europe.
- Example: Strava modified its heatmap feature in 2018 after GDPR concerns over tracking users’ workout locations.
Health startups that meet compliance requirements can scale faster by entering regulated markets like the U.S. and Europe.
Related: Ensuring Data Security in Health Apps: Proven Techniques for Developers
HIPAA & GDPR Compliance as a Competitive Differentiator
With growing public awareness of data privacy, health app users are becoming more selective about which platforms they trust. Companies that make security and transparency a selling point can stand out from competitors.
Examples of Privacy-Focused Companies Winning in the Market:
Apple HealthKit → Clearly communicates data privacy protections and doesn’t share health data without user consent.
Headspace (GDPR-compliant mindfulness app) → Implemented transparent consent policies, increasing EU user trust.
Signal (secure messaging app) → Built its reputation on end-to-end encryption & zero data collection.
By advertising HIPAA/GDPR compliance as a key feature, startups can differentiate themselves and attract privacy-conscious users.
Key Steps to Make Compliance Work for Your Business
Step 1: Adopt a Privacy-First Business Model
🔹 Design apps with Privacy by Design and Privacy by Default principles (required under GDPR).
🔹 Collect only necessary health data—avoid over-collection that increases compliance risks.
Step 2: Use HIPAA & GDPR-Compliant Infrastructure
🔹 Leverage secure cloud services (AWS HealthLake, Google Cloud Healthcare API).
🔹 Choose encrypted data storage and secure authentication methods (OAuth 2.0, multi-factor authentication).
Step 3: Market Compliance as a Feature
🔹 Display HIPAA/GDPR compliance badges on your website.
🔹 Create a transparent privacy policy that reassures users of data protection efforts.
Compliance isn’t just about avoiding fines—it’s a strategic asset that drives growth, improves user trust, and expands business opportunities.
Understanding HIPAA for Health Apps
Health and wellness apps that handle medical data, electronic health records (EHRs), or personal health information (PHI) must comply with HIPAA regulations. HIPAA is a U.S. law designed to protect the privacy and security of health data, ensuring that sensitive patient information isn’t misused or exposed.
For developers, failing to comply with HIPAA can lead to multi-million-dollar fines, loss of user trust, and even lawsuits. In this section, we’ll break down what HIPAA compliance means for health app developers, who needs to comply, and how to implement the necessary security measures in your mobile app.
What is HIPAA, and Who Needs to Comply?
HIPAA applies to any organization that handles health information. For mobile app developers, the key question is: Does your app collect, store, process, or transmit personal health data?
If YES, then your app falls under HIPAA compliance requirements and needs to follow strict data security protocols.
Who is Covered Under HIPAA?
HIPAA applies to two main groups that may involve health app developers:
| Entity Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Covered Entities | Organizations that provide healthcare services or process medical data. | Hospitals, doctors, health insurance providers. |
| Business Associates | Third-party vendors, software providers, or apps that handle Protected Health Information (PHI) on behalf of Covered Entities. | Mobile health apps, cloud storage providers, telemedicine platforms. |
Example: If your app integrates with an Electronic Health Record (EHR) system or collects patient-reported data, you are likely considered a Business Associate under HIPAA.
If your app transmits, stores, or interacts with PHI, you must be HIPAA-compliant.
Key HIPAA Compliance Requirements for Developers
HIPAA compliance isn’t just about encrypting health data, it requires technical, administrative, and physical safeguards to protect user information.
The Three Main HIPAA Rules
- Privacy Rule – Defines what health data is protected and who can access it.
- Security Rule – Ensures strong encryption, authentication, and data protection.
- Breach Notification Rule – Requires companies to report security breaches.
Technical Safeguards for HIPAA Compliance
| Requirement | What It Means for Developers | Implementation Example |
|---|---|---|
| End-to-End Encryption | All PHI must be encrypted at rest and in transit. | AES-256 encryption for stored data, TLS 1.2+ for transmitted data. |
| Access Controls | Limit access to sensitive data to only authorized users. | Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) – restrict access by role (e.g., doctor vs. patient). |
| Audit Logging | Track who accesses and modifies health data. | Maintain detailed logs of API requests and app activity. |
| Automatic Logouts & Session Timeouts | Prevent unauthorized access due to unattended devices. | Auto-log users out after inactivity (e.g., 10-minute timeout). |
| Secure Data Storage | Data must be stored on HIPAA-compliant cloud services. | Use AWS HealthLake, Google Cloud Healthcare API, or Azure for Healthcare. |
✅ Takeaway: Every health app must have built-in security measures to protect user data from leaks, unauthorized access, and hacking attempts.
Real-World HIPAA Violations: What Can Go Wrong?
Many health companies fail HIPAA compliance due to security oversights. Here are major case studies of what went wrong—and what you can learn from them.
Case Study 1: Anthem Inc. – $16M HIPAA Fine (2018)
🔹 The Breach: A cyberattack exposed 79 million patient records.
🔹 The Mistake:
- Lack of strong authentication – Hackers gained access using stolen credentials.
- No encryption on sensitive data stored in their database.
Lesson for Developers:
Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to prevent stolen credentials from being misused.
Encrypt all stored health data—even internally.
Case Study 2: Premera Blue Cross – $6.85M HIPAA Fine (2019)
🔹 The Breach: Hackers accessed 10.4 million medical records through a phishing attack.
🔹 The Mistake:
- No breach detection system in place.
- Delayed reporting of the breach to users.
Lesson for Developers:
Set up automated breach detection (e.g., AI-based anomaly detection).
Implement real-time alerts for unauthorized access attempts.
How to Make Your Health App HIPAA-Compliant
Step 1: Use HIPAA-Compliant Cloud Storage
- AWS HealthLake
- Google Cloud Healthcare API
- Azure for Healthcare
Step 2: Implement Secure APIs
- Use FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) API for structured health data exchange.
- Select third-party APIs that are HIPAA-certified (e.g., Twilio for secure messaging).
Step 3: Train Your Development Team on HIPAA Rules
- Educate developers on security best practices and data privacy regulations.
- Conduct regular security audits to ensure ongoing compliance.
✅ Takeaway: Following HIPAA guidelines prevents costly fines, protects user trust, and ensures legal compliance in the U.S. health market.
Understanding GDPR for Health Apps
For mobile health apps operating globally or serving European Union (EU) users, General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) compliance is mandatory. GDPR is one of the strictest data privacy laws in the world, governing how personal data is collected, stored, and shared.
Unlike HIPAA, which applies only to health-related data, GDPR covers all personal information, including fitness data, wearable device tracking, and general user analytics. Non-compliance can lead to massive fines, such as Google’s €50M GDPR penalty in 2019.
In this section, we’ll break down GDPR’s core principles, real-world compliance failures, and how developers can ensure compliance in their health apps.
What is GDPR, and Who Needs to Comply?
GDPR applies to any company handling personal data of EU citizens, even if the business is located outside the EU. If your app collects user names, location data, health metrics, or any personally identifiable information (PII) from European users, it must be GDPR-compliant.
Examples of GDPR-Regulated Health Apps:
- A U.S.-based fitness app that allows European users to track workouts.
- A meditation app collecting email addresses from EU users.
- A telehealth service storing medical records for EU-based patients.
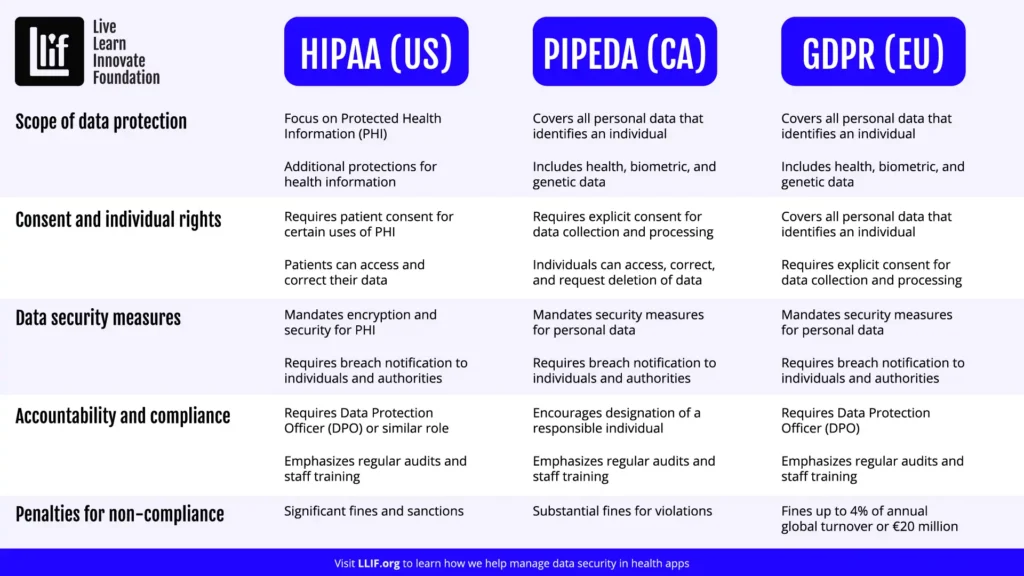
Key Differences Between GDPR & HIPAA
| Feature | HIPAA (USA) | GDPR (EU) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Only health-related data | All personal data (health, fitness, location, etc.) |
| User Consent | Not always required | Explicit opt-in required |
| Right to Data Deletion | Not included | Users can request their data be deleted (“Right to be Forgotten”) |
| Breach Notification Timeline | Within 60 days | Within 72 hours |
| Fines for Non-Compliance | Up to $1.5M per violation | Up to €20M or 4% of global revenue |
✅ Takeaway: GDPR covers a broader range of data than HIPAA and requires explicit user consent before collecting or processing information.
Key GDPR Compliance Requirements for Developers
GDPR follows seven core principles, which health app developers must incorporate into their systems.
The Seven GDPR Principles & How They Apply to Health Apps
| Principle | What It Means for Developers | Implementation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Lawfulness, Fairness & Transparency | Users must know what data is collected and how it’s used. | Clear privacy policy and opt-in consent. |
| Purpose Limitation | Apps can only collect data for a specific reason. | Don’t collect unnecessary personal details. |
| Data Minimization | Store only the minimum amount of user data needed. | Avoid collecting extra data fields. |
| Accuracy | Users can update or correct their data. | Allow profile edits & data modification requests. |
| Storage Limitation | Don’t keep data longer than necessary. | Implement automated data deletion policies. |
| Integrity & Confidentiality | Ensure secure storage & access. | Use AES-256 encryption & multi-factor authentication (MFA). |
| Accountability | Companies must prove compliance. | Keep detailed data logs and compliance records. |
✅ Takeaway: Developers must actively design apps for GDPR compliance, ensuring transparent data policies, minimal data collection, and strong security protections.
Real-World GDPR Violations: What Can Go Wrong?
Many tech giants and startups have faced massive GDPR fines due to poor data protection measures. Let’s explore major case studies and what developers can learn from them.
Case Study 1: Google (€50M GDPR Fine, 2019)
🔹 The Violation: Google failed to properly inform users how their personal data was being processed for advertising purposes.
🔹 What Went Wrong?
- No clear opt-in process for data collection.
- Vague privacy policies without easy-to-understand explanations.
Lesson for Developers:
Clearly state what data is collected, why, and how it’s used in simple language.
Ensure users actively opt-in before collecting data.
Case Study 2: Facebook (WhatsApp) – €225M GDPR Fine (2021)
🔹 The Violation: WhatsApp didn’t properly disclose how it shared user data with its parent company, Facebook.
🔹 What Went Wrong?
- Users had no control over how their data was shared.
- No option to opt out of data processing.
Lesson for Developers:
Allow users to choose what data they share (e.g., opt-out for third-party tracking).
Make privacy settings easy to access in the app.
How to Make Your Health App GDPR-Compliant
Step 1: Implement User Consent Management
- Use explicit checkboxes (No pre-checked consent boxes!).
- Provide granular consent options (e.g., separate choices for analytics vs. marketing tracking).
Step 2: Enable User Data Access & Deletion
- Allow users to request a copy of their data.
- Implement “Right to Be Forgotten” – users should be able to delete their accounts and data.
Step 3: Secure Data Storage & Transfer
- Store data only in GDPR-compliant cloud services (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure).
- Use end-to-end encryption for user health data
Step 4: Establish a Breach Notification System
- Apps must notify regulators & users within 72 hours of a data breach.
- Use automated breach detection to spot security threats.
✅ Takeaway: GDPR forces businesses to be transparent with user data—prioritizing user control, security, and fast breach response.
The Business Benefits of GDPR Compliance
User Trust & Brand Reputation – Privacy-conscious consumers prefer apps that respect their data rights.
EU Market Access – GDPR compliance allows entry into 31 European countries.
Lower Legal Risk – Avoids multi-million-dollar fines & lawsuits.
How to Secure Your Health App: Implementation Checklist
Step 1: Encrypt All User Data → Use AES-256 for storage and TLS 1.2+ for transmission.
Step 2: Implement Strong Authentication → Require MFA and OAuth 2.0 for API access.
Step 3: Use GDPR/HIPAA-Compliant APIs → Verify vendors before integrating their services.
Step 4: Deploy Intrusion Detection & AI Security Monitoring → Prevent real-time security threats.
Step 5: Create a Breach Response Plan → Ensure fast reporting and containment of any security incidents.
✅ Takeaway: By implementing these security measures, health app developers can reduce risks, protect user data, and ensure compliance with global data protection laws.
Common Mistakes Developers Make & How to Avoid Them
Even with the best intentions, many health app developers unknowingly introduce security vulnerabilities that lead to data breaches, compliance failures, and legal penalties. The complexity of HIPAA, GDPR, and security best practices makes it easy to overlook critical safeguards, especially for startups and small development teams.
We’ll break down common security mistakes, real-world examples of companies that suffered major consequences, and practical solutions to ensure your health app remains secure and compliant.
Common Security Mistakes in Health App Development
Mistake #1: Not Implementing Strong Data Encryption
🔹 The Risk: Storing or transmitting user health data without encryption leaves it vulnerable to hackers.
Real-World Example:
- MongoDB Misconfiguration (2019):
- An unsecured database exposed 2.7M medical records online, accessible without a password.
- The data included names, treatment history, and insurance details.
- Cause: The developers did not configure proper encryption or access controls.
Solution for Developers:
- Use AES-256 encryption for data at rest (stored data).
- Use TLS 1.2+ encryption for data in transit (API communication).
- Avoid storing unencrypted health data in local app storage.
Mistake #2: Weak Authentication & Access Controls
🔹 The Risk: Allowing weak passwords, lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA), or unrestricted access can expose sensitive health data to unauthorized users.
Real-World Example:
- Anthem Inc. HIPAA Breach ($16M Fine, 2018):
- Hackers used stolen credentials to gain access to Anthem’s system, exposing 79 million patient records.
- The system did not have multi-factor authentication (MFA) enabled, making it easy for attackers to log in.
Solution for Developers:
- Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for users and administrators.
- Use OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect for secure authentication.
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to restrict who can access sensitive data.
Mistake #3: Failing to Obtain Proper User Consent
🔹 The Risk: Collecting personal health data without explicit user permission violates GDPR and can result in legal action.
Real-World Example:
- Google’s GDPR Fine (€50M, 2019):
- Google was fined for failing to clearly explain how it collected and processed user data.
- Users were not given an explicit opt-in choice for data tracking.
Solution for Developers:
- Provide clear, specific opt-in prompts for data collection.
- Use separate consent checkboxes for different data uses (analytics, marketing, health tracking).
- Allow users to withdraw consent at any time (required under GDPR).
Mistake #4: Ignoring Third-Party Vendor Security
🔹 The Risk: Integrating third-party APIs, SDKs, or cloud storage without vetting security compliance can lead to breaches.
Real-World Example:
- American Medical Collection Agency Breach (2019) – $21M HIPAA Lawsuit
- A third-party billing service used by Quest Diagnostics & LabCorp was hacked, exposing 25 million patient records.
- The breach was due to weak security practices at the vendor—not the healthcare providers themselves.
Solution for Developers:
- Use HIPAA/GDPR-compliant third-party services (e.g., AWS HealthLake, Google Cloud Healthcare).
- Require Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) from all vendors handling Protected Health Information (PHI).
- Perform regular security audits on third-party APIs and SDKs.
Mistake #5: No Breach Detection or Incident Response Plan
🔹 The Risk: Many companies don’t have real-time monitoring for security breaches, leading to delayed responses and severe penalties.
Real-World Example:
- Excellus Health Plan Breach ($5.1M Fine, 2021):
- Hackers accessed the system for over 20 months without detection, exposing 9.3M records.
- The company had no automated breach detection system in place.
Solution for Developers:
- Deploy intrusion detection systems (e.g., AWS GuardDuty, Splunk, IBM QRadar).
- Implement real-time security alerts for unauthorized access.
- Have an incident response plan in place, including 72-hour breach reporting (for GDPR compliance).
How to Fix These Mistakes: The Secure Health App Development Checklist
Step 1: Encrypt All Health Data → Use AES-256 for storage & TLS 1.2+ for API transmission.
Step 2: Require Strong Authentication → Implement MFA and OAuth 2.0 for secure logins.
Step 3: Use GDPR/HIPAA-Compliant APIs → Vet all third-party vendors for security certifications.
Step 4: Enable User Consent Management → Provide clear opt-in options for data collection.
Step 5: Deploy AI-Powered Threat Monitoring → Detect unauthorized access & data breaches in real-time.
Step 6: Implement a Breach Response Plan → Ensure fast containment & reporting of security incidents.
✅ Takeaway: Health apps must proactively address these common mistakes to avoid regulatory fines, security breaches, and reputational damage.
The Future of Health App Compliance
As technology evolves, so do regulatory frameworks and security expectations for health and wellness apps. The healthcare industry is experiencing a surge in AI-driven diagnostics, wearable health tracking, and decentralized data storage, all of which introduce new privacy challenges and compliance requirements.
In this section, we’ll explore emerging trends, upcoming regulations, and how health app developers can stay ahead in the ever-changing compliance landscape.
The Shift Toward Global Data Protection Standards
Data privacy laws are no longer regional issues—governments worldwide are enacting stricter regulations similar to HIPAA and GDPR.
Upcoming Regulations to Watch:
- EU’s AI Act (Expected 2025-2026) → Will regulate AI-based health apps to ensure algorithmic transparency and user safety.
- U.S. National Privacy Law (Proposed) → Potential federal law to unify state-level data privacy rules (similar to GDPR).
- China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) → More restrictive than GDPR, requiring data localization for apps operating in China.
Developers must design apps with compliance flexibility, allowing for regional adjustments as new laws emerge.
AI & Machine Learning in Health Apps: New Compliance Risks
AI-powered health apps are transforming patient diagnostics, personalized fitness coaching, and mental health support. However, AI introduces significant compliance concerns, including data bias, informed consent, and transparency.
Key AI Compliance Challenges:
- Explainability → Users must understand how AI makes health predictions (e.g., why an AI-powered diet app recommends certain foods).
- Bias & Fairness → AI models must be tested for biases to avoid discrimination in predictive health analysis.
- Data Privacy → AI models must be trained on anonymized health data to protect patient identities.
Example:
- Google’s AI-powered dermatology app faced criticism for potential racial bias due to insufficient diversity in training data.
- IBM Watson Health (discontinued in 2022) → Struggled with AI accuracy issues in cancer treatment recommendations, raising compliance concerns.
Future AI regulations will require more transparency, forcing developers to document and audit AI decision-making processes.
Blockchain & Decentralized Health Data Storage
Blockchain technology is emerging as a secure alternative to centralized health data storage, offering tamper-proof records and enhanced privacy.
How Blockchain Can Enhance Compliance:
- Decentralized Storage → Eliminates single points of failure, reducing the risk of massive breaches.
- User-Controlled Health Data → Patients could own and manage their health records, granting access only when necessary.
- Immutable Audit Trails → Creates permanent, verifiable records for regulatory reporting.
Example:
- Estonia’s National Health Records System uses blockchain to secure patient data and track access logs.
- BurstIQ (U.S. startup) → Uses blockchain for secure health data sharing between patients, doctors, and researchers.
Blockchain adoption in health apps is growing, but developers must balance decentralization with regulatory compliance.
The Future of User Consent & Data Ownership
Users are demanding greater control over their personal health data, which is leading to stricter consent management laws.
What’s Changing:
- Granular Consent Options → Users will soon be able to control access to specific data types (e.g., allowing fitness tracking but not heart rate monitoring).
- Data Portability Requirements → Regulations will require easy data export & transfer between apps.
- Zero-Data Retention Policies → Some privacy advocates push for temporary health data storage, deleting records after predefined timeframes.
Example:
- Apple’s Health App allows users to revoke third-party access to their health data at any time.
- Sweden’s GDPR Implementation requires that users can request a copy of all personal data collected by a company.
Developers should offer clear, user-friendly privacy settings that empower users to control and manage their own health data.
How Developers Can Future-Proof Their Health Apps
- Adopt Privacy by Design → Build apps with compliance-first development strategies.
- Implement Transparent AI Models → Ensure users understand AI-driven recommendations.
- Stay Updated on Global Regulations → Monitor new compliance laws to maintain international market access.
- Embrace Decentralized Data Models → Explore secure blockchain-based health data solutions.
- Enhance User Data Controls → Provide fine-grained data consent options to improve privacy transparency.
The future of health app compliance will be driven by AI, blockchain, global privacy laws, and increased user data control. Developers must stay ahead of these changes to build secure, compliant, and user-trusted applications.
Related: Get a headstart on your health app build by partnering with a compliant and nonprofit data lake.
Conclusion: Why Compliance is a Competitive Advantage for Health App Developers
The health and wellness app industry is evolving rapidly, and so are the regulatory expectations around data privacy, security, and ethical AI usage. While compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and emerging global regulations may seem like a burden, forward-thinking developers recognize it as a strategic advantage that enhances user trust, investor confidence, and market access.
✅ HIPAA and GDPR Compliance is Essential – If your app handles personal health data, compliance is not optional. Failing to meet regulations can result in fines, lawsuits, and loss of user trust.
✅ Data Security is the Foundation of Compliance – Encryption, authentication, role-based access controls (RBAC), and API security are critical for protecting user health data from breaches.
✅ The Most Common Mistakes Are Avoidable – Unencrypted data, weak authentication, poor third-party security, and no breach response plan are common pitfalls that developers must address early in the development process.
✅ The Future of Compliance is AI, Blockchain, and User Control – AI-driven health apps, decentralized data storage, and granular user consent will shape the next generation of data protection laws. Developers should prepare for these changes now to stay ahead of the curve.